
Labour Market Cooling Down: Hiring Remains Positive, but with Less Momentum
Following optimistic forecasts at the beginning of the year, employers are taking a more cautious approach to workforce planning in the second half of 2025. According to the latest "Salary and Employment Trends – H2 2025" survey, more than two-thirds of companies (70.93%) do not plan to change salaries, while the Net Employment Outlook (NEO) slightly declines to +41.91%. Despite market cooling, the hiring climate remains positive, and talent shortages continue to push companies to seek long-term solutions.
Key findings from the research:
In H2 2025, 28.72% of employers plan to increase salaries, mostly up to 5%.
84% of employers foresee no significant changes in employee benefits, while 14% plan to increase or introduce new ones.
The main reason for salary increases, cited by 65% of employers, is to retain current staff.
The greatest hiring difficulties in H1 2025 were reported in production departments, followed by maintenance, field service, installation and construction, and logistics/warehouse.
The Net Employment Outlook for H2 2025 stands at +41.91%.
Employers Remain Cautious About Salaries and Benefits
The research shows that 70.93% of employers are not planning salary changes in H2 2025. 28.72% will increase salaries, while only 0.35% plan to reduce them. Among those planning increases, around one-third (32.53%) will apply the raise to all employees.
A clear seasonal trend is visible: salary increase expectations are typically higher in the first half of the year (H1) than in the second (H2). The most notable spike occurred in H1 2023 (68.79%), followed by the sharpest drop to 26.70% in H2 2023.
The H2 2025 forecast (28.72%) is closest to that of H2 2023 (26.70%). Compared to the same period last year (H2 2024), the percentage of employers planning salary increases dropped from 36.20% to 28.72%.
Graph: What salary changes do employers plan in H2 2025?

Retention Remains a Priority
As the competition for talent continues, companies are strengthening employee retention strategies. More than 65% of employers will raise salaries primarily to retain current staff, while 26.51% will do so to attract new talent. Inflation also plays a role: around 40% of employers cited inflation-related concerns as the reason for increasing wages, in order to preserve employees’ purchasing power.
Employers who do not plan salary changes mostly cited raises already granted in 2024 or early 2025, challenging market conditions, and high operational costs.
Additionally, 80% of employers do not anticipate major changes to non-wage benefits or incentives. Among the most common benefits already offered are anniversary bonuses, team building events, and performance-based rewards, reported by nearly 70% of participating companies.
Holiday Bonus (Regres) in 2025
The average holiday bonus paid by participating companies in 2025 was €1,946.48, with a median value of €2,000. 83.15% of employers reported higher holiday bonus than the previous year, while 16.85% paid less.
Employment Outlook Remains Positive
The Net Employment Outlook for H2 2025 remains positive at +41.91%, though slightly down from +43.65% in H1 2025.
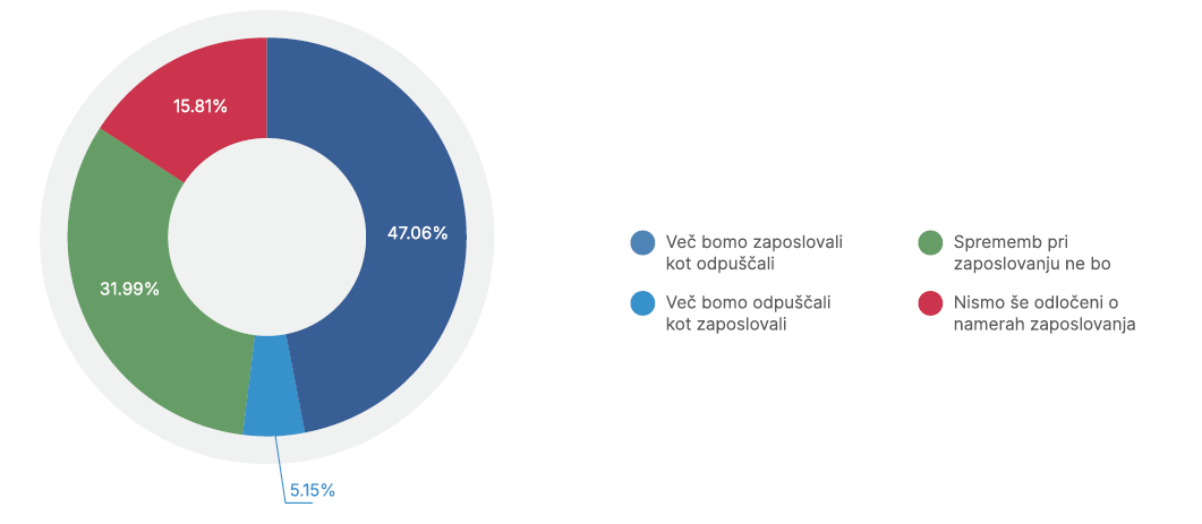
Roughly 47.06% of employers plan to hire more than they will lay off, while 5.15% expect more layoffs. 31.99% foresee no changes, and 15.81% are still undecided.
Graph: What are your hiring intentions for H2 2025?
Looking at specific industries, all sectors report a positive Net Employment Outlook, indicating that most employers plan to hire. The most optimistic industries include healthcare and pharmaceuticals, tourism and hospitality, mechanical engineering, manufacturing, and construction.
Note: Net Employment Outlook (NEO) is calculated by subtracting the percentage of employers expecting to reduce staff from those expecting to increase it. A positive NEO indicates that more employers anticipate hiring than reducing headcount.
Regional Hiring Trends: Insights from Six Southeast European Countries
For the first time, Manpower conducted a regional Recruitment Trends 2025 survey, covering over 1,100 employers across Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary, Serbia, Bulgaria, and Bosnia & Herzegovina.
Graph: Which channel helped you find the most suitable candidates in 2025?
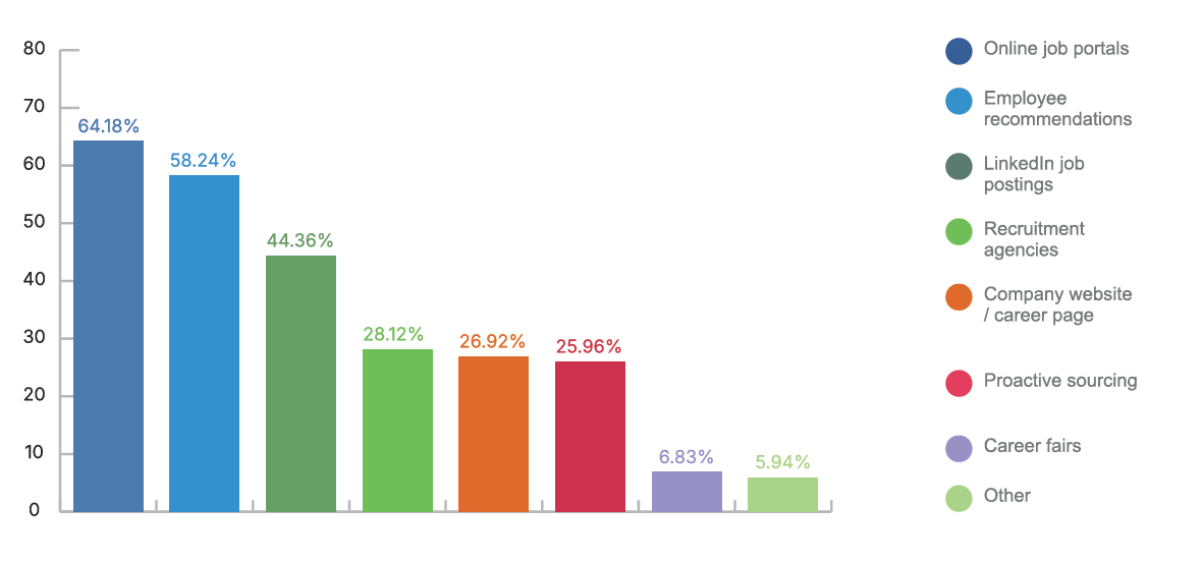
The report reveals that companies across the region have adapted to the talent shortage by expanding their sourcing strategies. Online job platforms dominate as the most used hiring channel in every participating country, mentioned by 64.18% of respondents.
The top recruitment challenge in the region, reported by 69.17% of employers, is the difficulty in finding suitable candidates, signaling a persistent talent shortage across industries and job roles.
Regarding time-to-hire, only 27.28% of companies fill roles within one month. The majority hire within 1–2 months (41.62%). Key decision-making factors include cultural/team fit (average score 4.19/5), followed by salary expectation alignment (4.03) and professional qualifications (4.02).
Use of Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment Still Limited
Despite growing interest in digital tools, the use of AI in recruitment remains relatively low across Southeast Europe. On average, only 21.47% of employers currently use AI in their hiring processes. Among the companies using AI, the vast majority (85%) apply it to draft job ads and descriptions. Other use cases are more selective and include CV pre-screening, internal analytics (e.g., turnover and satisfaction tracking), onboarding support, and chatbot-based candidate communication.
About the “Salary and Employment Trends” Report – H2 2025
The Salary and Employment Trends – H2 2025 report provides insights into labour market conditions, employee turnover over the past year, hiring intentions, planned salary adjustments, and benefit changes for 2025. It also includes comparisons of salary change trends over the past three years.
For more insights on labour market trends, salaries, hiring patterns, and salary benchmarks, visit: https://www.raziskave-manpower.com/




